Kingdom: Protista
Stramenopila
General Characteristics
_
- Stramenopila is a group that includes brown algae, kelps, diatoms, and water molds
- Generally live in marine environments
- Even the giant brown algae lack the complex vascular systems of land plants
- Water molds (oomycetes) can be parasitic
Diatoms
_
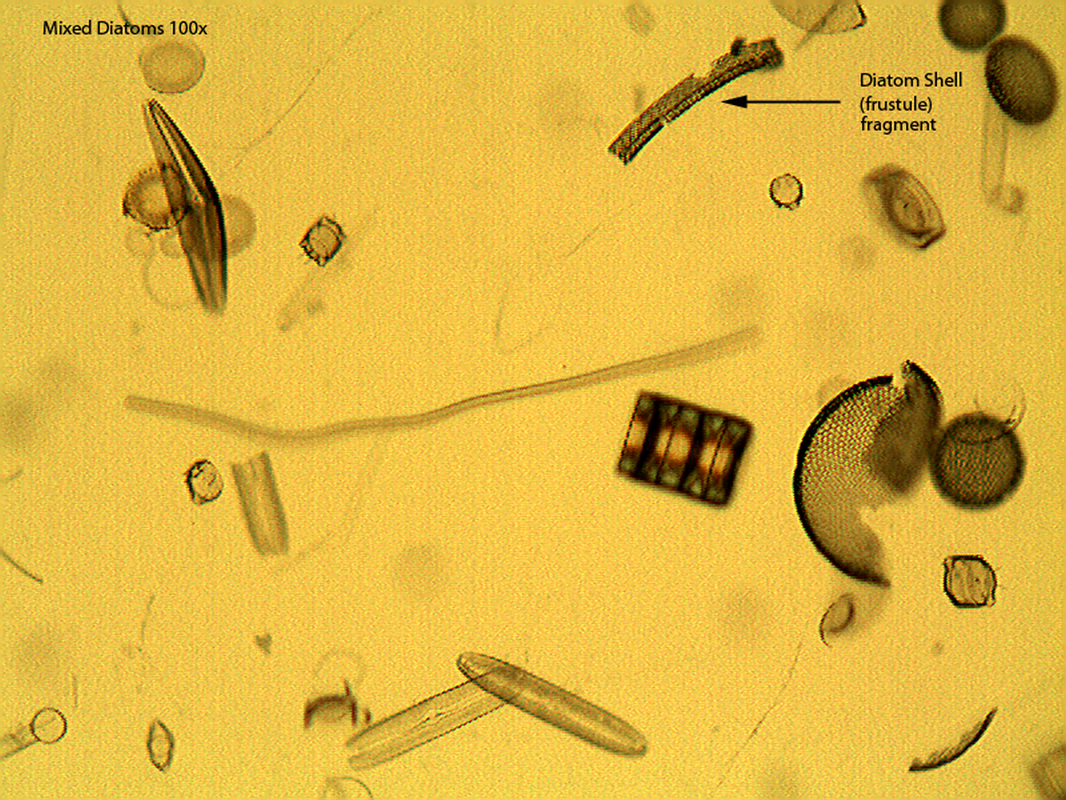
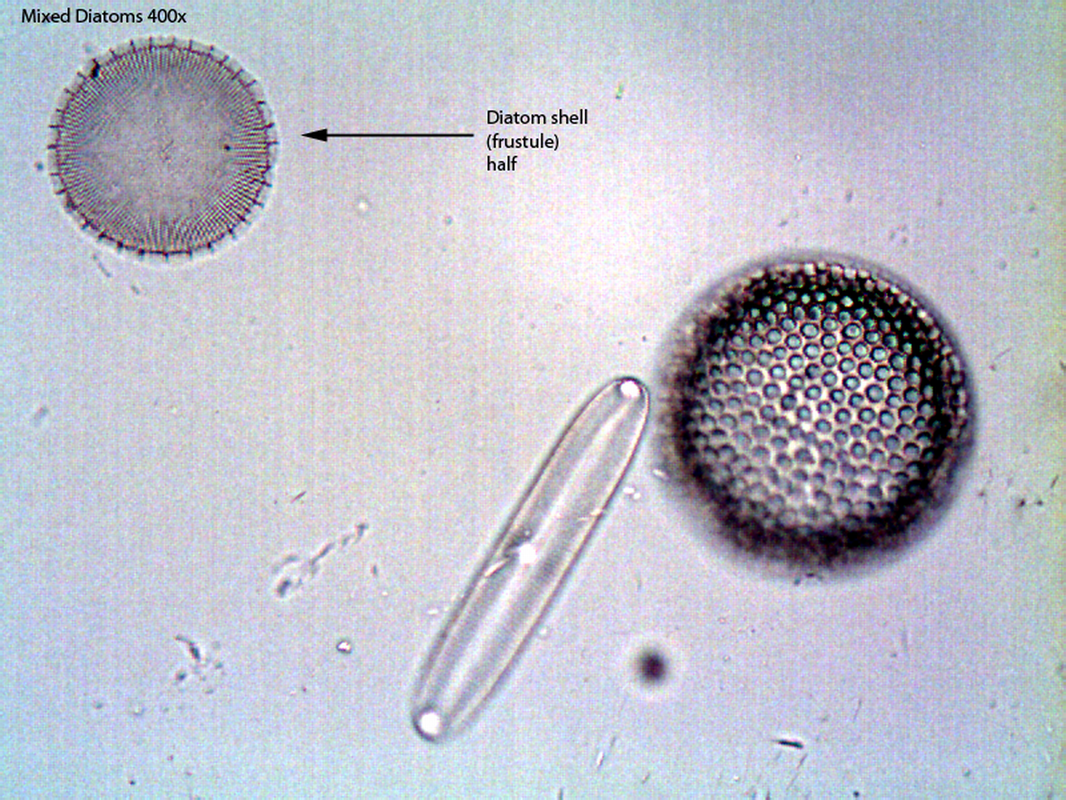
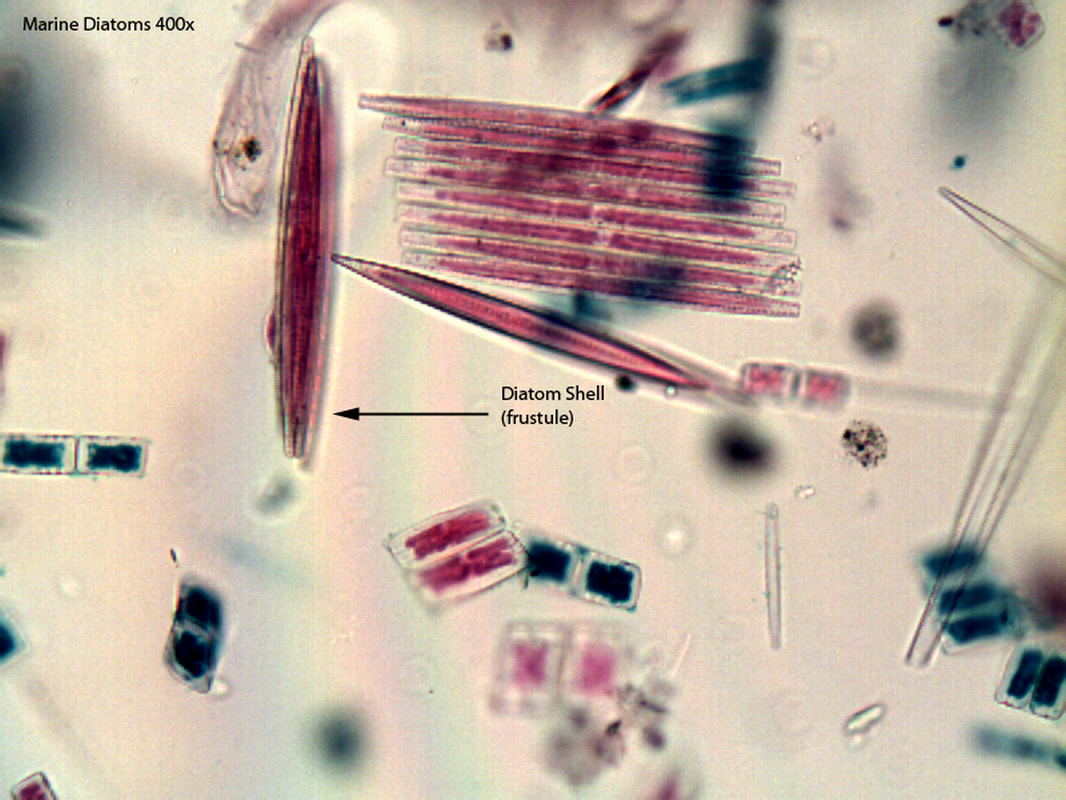
- Uniquely silica-shelled unicellular algae.
- Diatoms produce two shells out of silica that fit closely together, called frustrules
- Produce food through photosynthesis
- Some diatoms move using two long grooves called raphes
- Shells vary wildly in shape
Fucus
_
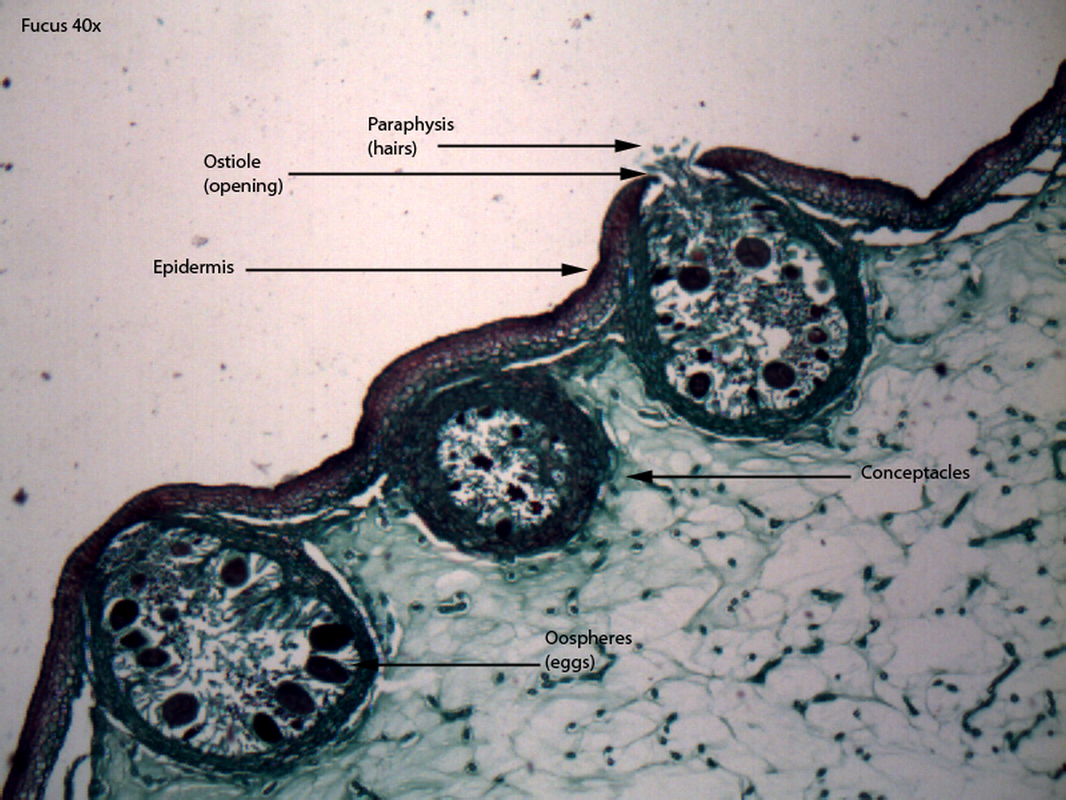
- A common kelp species found on rocky seashores.
- Each plant produces both male and female reproductive structures
- Those take the form of conceptacles, cup-shaped structures with ostioles (openings) guarded by paraphyses (hairs) out to the environment
Brown Algae